
La décaféination dite "Canne à sucre", au cœur de l'usine Descafecol
Tous les procédés de décaféination doivent être synonymes de cafés de bonne qualité. L'usine Descafecol, en Colombie, fait partie des rares entreprises à savoir décaféiner un café, sans le dénaturer.
La méthode Descafecol
L’usine Descafecol est située à Manizales, dans l'une des principales zones de cafés de spécialité en Colombie. Elle a été inaugurée en 1988 et constitue l'unique usine de décaféination en Colombie.
Le procédé de décaféination à l'Acétate d'Ethyle, dérivé de la canne à sucre
Mauricio Jaramillo, Directeur commercial, et Sven Dabelstein, Directeur général, nous ont expliqué comment l'Acétate d'Ethyle agit pour extraire la caféine. C'est un composant naturel de certains fruits, en particulier chez les fruits mûrs.
L’acétate d’éthyle, comme solvant dérivé de la canne à sucre, lorsqu’il est utilisé dans les bonnes conditions et quantités, est un excellent extracteur sélectif de la caféine.
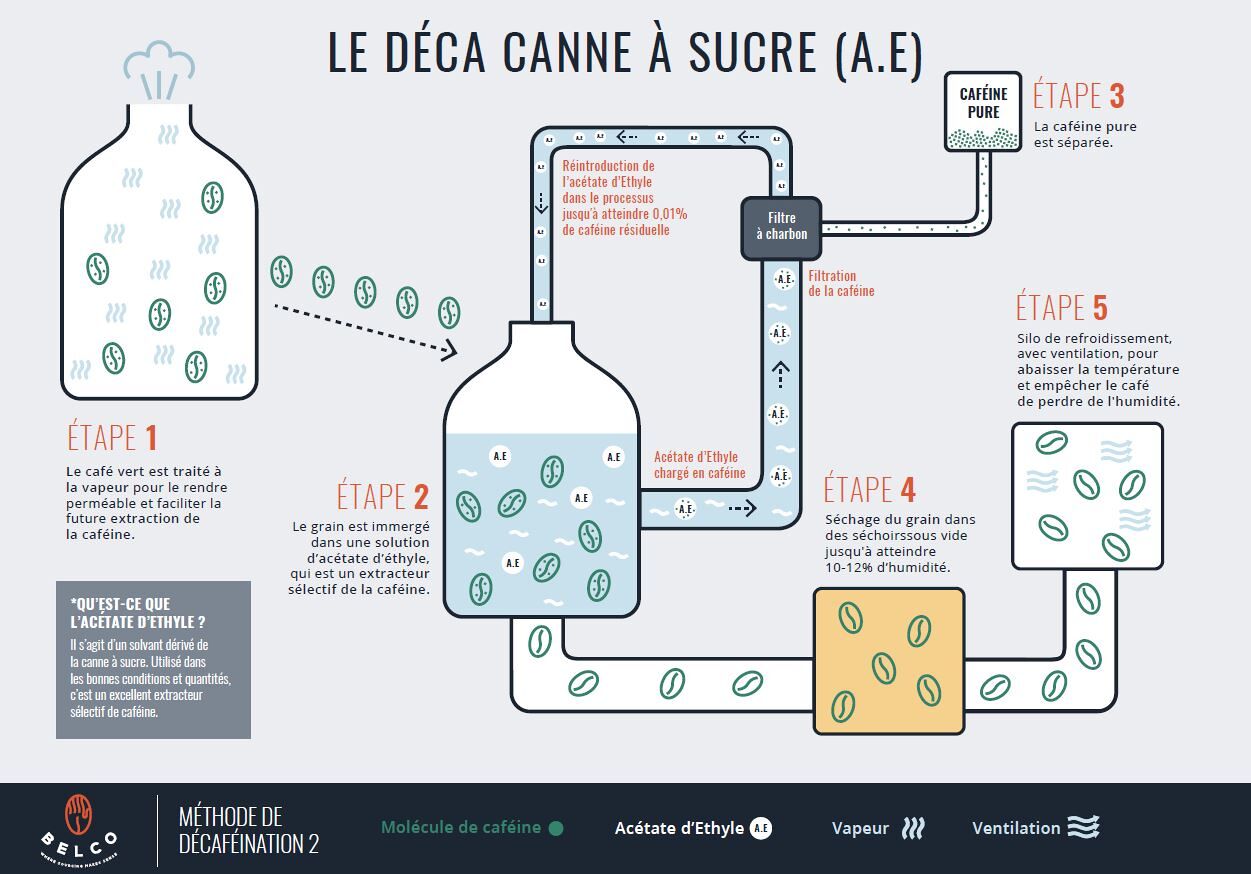
Les 6 étapes du procédé Descafecol
Traitement à la vapeur
La première étape consiste à exposer le grain à un traitement à la vapeur d'eau visant à ouvrir les membranes du grain et à faciliter l'extraction future de la caféine.
L’extraction
Le grain est immergé dans une solution d’acétate d’éthyle, qui est un extracteur sélectif de la caféine. La caféine contenue dans le grain de café va alors migrer vers le solvant liquide, qui sera transporté vers une autre cuve.
À cette étape, l'acétate d'ethyle chargé en caféine sera filtré et réintroduit au procédé pour extraire de nouveau la caféine du grain, jusqu'à atteindre 0,01% de caféine résiduelle.
Séparation de la caféine pure
La caféine pure est séparée.
Séchage
Le processus de séchage est effectué dans des séchoirs sous vide, ce qui permet un séchage rapide et homogène
Silo de refroidissement
Le café est placé dans un silo avec ventilation pour abaisser la température et à empêcher le café de perdre de l'humidité.
Et enfin...
Polissage du grain
La décaféination dite "Canne à sucre", au cœur de l'usine Descafecol
Outre le traitement de la décaféination, deux types de contrôle de la qualité sont effectués dans leur laboratoire. Le premier consiste en une analyse physique et chimique du grain visant à mesurer la quantité de caféine résiduelle qui, en règle générale, ne peut être supérieure à 0,1% et que le résidu de l'Acétate d’Ethyle ne dépasse pas 20 ppm.
Dans une seconde analyse, les propriétés organoleptiques du café seront mesurées, en comparant leurs profils avant et après le processus de décaféination.
Pour terminer
Quelques données liées à l’extraction
Il convient aussi de noter que ces étapes dépendent du temps et d’une certaine saturation de caféine et de cire dans le liquide (EA). Cependant, la réutilisation aura ses limites car, dans le même laboratoire Descafecol, la détérioration de sa structure chimique sera analysée et, en fonction des résultats, son utilisation ou son élimination sera définie.
Qu'en est-il de la caféine résiduelle ?
La caféine récupérée lors de ce procédé a beaucoup de valeur dans l'industrie pharmaceutique. Elle sert pour les boissons énergisantes, mais aussi en tant qu'insecticide naturel. Chez Descafecol, la caféine qui est récupérée est une caféine naturelle sans raffinage.
Café biologique et procédé EA
La question de l'utilisation de l'EA pour la production de café biologique a été longuement discutée dans l'industrie. Descafecol affirme fermement que l'EA est un composant totalement naturel et qu'il peut sans souci être utilisé pour les cafés certifiés bio.
Vous avez aimé cet article ? Partagez-le avec votre communauté :
